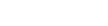Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard have driven unprecedented interest in and understanding of AI and machine learning’s (ML’s) potential. The time-savings that users have enjoyed by offloading writing or organizational tasks to GenAI have thrust these tools to the top of many businesses’ “must-have” lists, and understandably so. They can free up workers’ time to focus on tasks that require a human touch—and execute high-priority tasks with superhuman precision.
Despite their impressive outputs, though, these high-profile tools are just the tip of the iceberg regarding what AI can—and will—do for businesses. The principles that underlie them have nearly unlimited applications, and many are perfectly suited to high-precision, volume-based processes like those found in manufacturing facilities.
Table of Contents
AI In Manufacturing
Though solutions for increased efficiency and operational enhancement have long been helping manufacturers drive their businesses forward, the capabilities of tools supported by AI and ML go far beyond anything the industry has seen before. Building on the foundation of their software forebearers, ML and AI solutions can take stock of a business’s past, keep an eye on its operational present, and predict future needs and issues with startling accuracy.
Here are some of the incredible ways that AI is reinventing what it means to optimize operations:
1. Optimized Production Scheduling with AI-powered Decision-Making:
Armed with the right data, AI-powered decision-making tools can help manufacturers optimize their production processes to increase yields without impacting quality or labor allocation. MES platforms with algorithmic production scheduling components—like the one in TrakSYS™—see AI strategically reference things like historical performance, real-time asset availability, and on-hand inventory to create and propose optimized production schedules.
In instances where equipment is not able to integrate directly with the MES, TrakSYS Smart Devices can be used to capture analog, digital, or serial data from those assets, which ensures a lack of direct connectivity doesn’t become a barrier to entry for unlocking AI-enhanced scheduling.
These tools can also automate ordering and fulfillment tasks, freeing up employees’ time to focus on additional time-sensitive tasks. When integrated with an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, production scheduling platforms can automate order management, job assignments, quantity specifications, and progress tracking. Similarly, predictive alert systems can notify managers and production workers of potential disruptions or events that need attention. Event tracking and management tools use real-time production data to analyze on-floor events, alert teams to possible disruptions, and offer actionable solutions to help them get ahead of delays.
While some non-AI-based software can help automate scheduling, having a system that can do it in real time and adjust its approach based on continuous feedback is a game-changer for operations. The adaptability of these tools can lead to far-reaching benefits, from reduced lead times to improved resource utilization and production capacity—all of which can lead to better business outcomes.
2. Improved Quality Control with AI-powered Vision Systems:
Getting ahead of quality issues can reduce materials waste, make production more efficient, improve customer satisfaction, and safeguard brands’ reputations. That said, one of the most promising—and least well-known—AI applications for manufacturing is computer vision. These systems use advanced AI models to “watch” video feeds for different events and alert teams when they occur.
In practice, the AI model is trained to recognize what items should look like at any given part of the process, enabling the software to alert workers to variations from that ideal should they arise.
By positioning cameras throughout the production line, manufacturers can now enhance their quality control (QC) programs with extra sets of extra-sensitive virtual eyes.
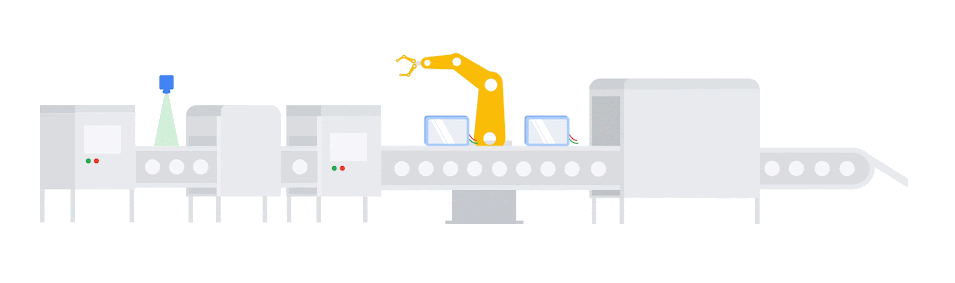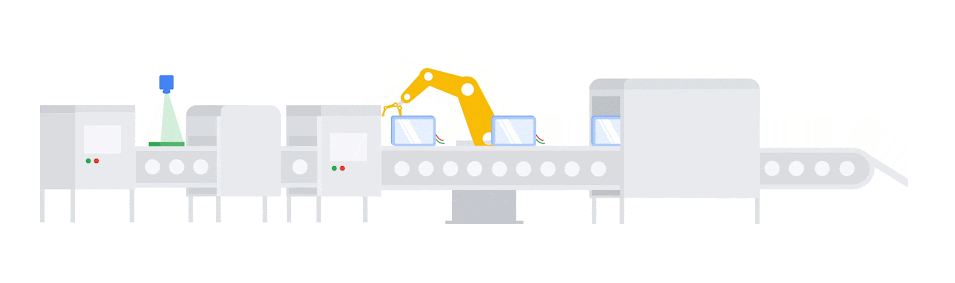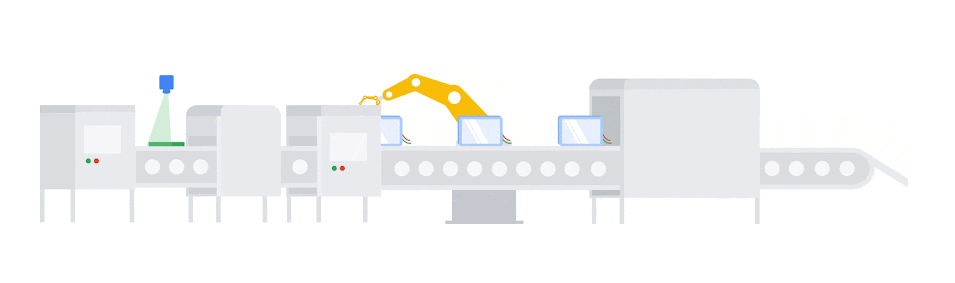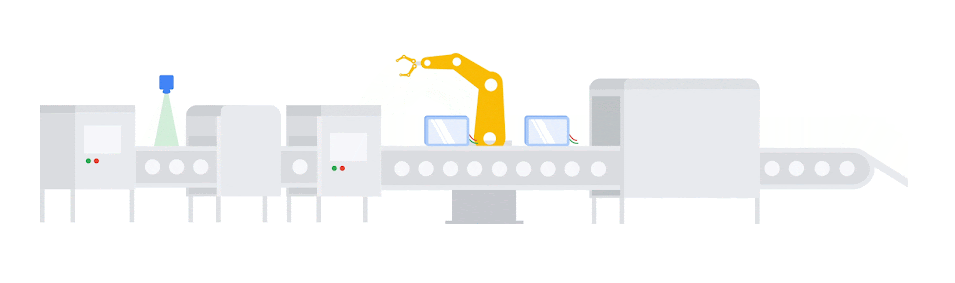
3. Predictive Maintenance with Machine Learning Algorithms:
Managing maintenance schedules can be an overwhelming task, especially when equipment unexpectedly breaks down in the middle of production. Machine learning systems within MES platforms are helping manufacturers get ahead of these unforeseen disruptions. While predictive maintenance solutions have been popular for some time, the addition of IIoT monitoring and advanced AI/ML capabilities allows manufacturers to fine-tune predictive maintenance programs based on actual use rather than machine age and estimations.
Much like the algorithmic scheduling tools described above, predictive maintenance suites use enterprise and monitoring data to analyze equipment performance, model production needs, and alert teams to any signs that maintenance issues might soon arise. By tracking things like vibration, temperature, oil, pressure, and more, these systems can predict when equipment will need service with more precision, which allows facility managers to build downtime into their plans rather than react as it happens.
Manufacturers that use AI-based predictive maintenance tools often see downtime and repair costs drop sharply, but that’s not the only benefit nor the most compelling. Folding AI into predictive maintenance plans can further extend the lifespan of costly industrial equipment, allowing manufacturers to make the most of their investments.
4. Optimized Supply Chain Management with AI-driven Demand Forecasting:
Anticipating supply chain issues is a critical capability in today’s market. Case-in-point: Parsec’s State of Manufacturing survey found that more than one-third (36%) of North American manufacturers see today’s market as very or extremely challenging, and less than half (47%) are prepared to handle the supply chain landscape.
AI tools with access to market- and industry-level datasets can analyze trends, material availability, and sales data to predict future demand. With the right data, it can also flag conditions that might indicate material scarcities or delays in fulfillment, giving teams a head-start on identifying alternative vendors. This allows businesses to get ahead of potential concerns before they impact production. Manufacturers that lean into this process are able to optimize their inventory and material management practices more effectively, which means less waste, fewer missed opportunities, and better relationships with suppliers and customers.
Of note to leaders considering investments in these tools are their compounding returns. While it’s likely that manufacturers will see results fairly quickly after implementation, the value of ML and AI investments grows over time as improvements build upon one another and databases grow. The larger the reference dataset, the more precise predictions the tool can provide and the more opportunities for optimization arise, building on one another to deliver continuous improvements.
TrakSYS for Intelligent, Automated Manufacturing
The digitalization of manufacturing operations has been underway for some time now, but emerging technologies are poised to take the power of connected enterprises to the next level. AI and ML have the capabilities to turn operational data into optimizations that touch every aspect of a business—like scheduling, QC, supply chain management, and maintenance—and do it with more precision, accuracy, and specificity than ever before.
To learn more about the ways TrakSYS can improve your manufacturing operations and see an AI-enabled factory in action, explore our interactive digital factory experience.